What is a Lamination Machine and How Does It Work?
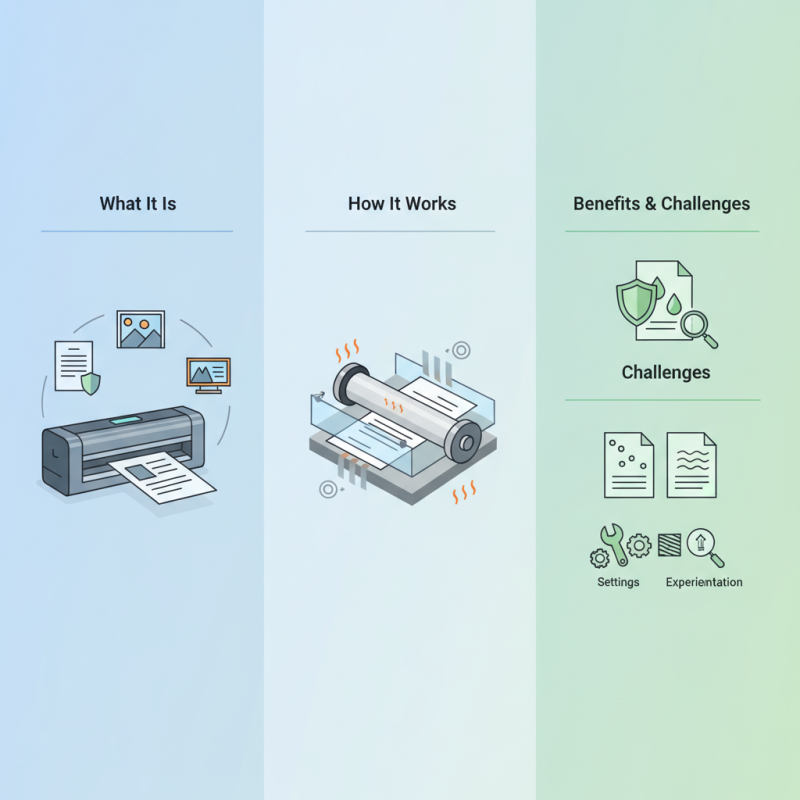
A Lamination Machine is an essential tool in various industries. It provides a protective layer over items like documents, photos, and signs. This process not only enhances durability but also improves appearance.
Understanding how a lamination machine works can help users maximize its potential. The machine uses heat and pressure to bond plastic film to the surface of the material. The result is a glossy finish that shields against wear and tear.
Yet, using a Lamination Machine isn't always straightforward. Problems can arise, such as bubbles or uneven lamination. Users must pay close attention to settings and materials. Experimentation is key. Embracing these challenges can lead to better results and more efficient lamination techniques.
What is a Lamination Machine?
A lamination machine is a device designed to preserve documents or images by encasing them in a protective layer. This process involves the application of heat and pressure to seal a plastic film around a paper. The film enhances durability and resistance to elements like moisture and dirt. Many businesses utilize this technology to protect important documents, such as ID cards, menus, and certificates.
Recent industry studies indicate the lamination market is growing significantly. By 2025, the market size is expected to rise to over $36 billion globally. This increase reflects the demand for more durable products across various sectors. Companies often strive for efficiency, but many overlook the machine's maintenance needs. Regular upkeep can prevent issues like uneven sealing or bubbles. If neglected, these problems can lead to increased costs and wasted materials.
In the laminating process, the choice of film thickness is crucial. A thicker film provides more protection but can affect flexibility. Many users disregard these details, leading to unsatisfactory results. Finding the right balance is essential for successful lamination. It's not just about sealing documents; it's about producing a quality end product that meets expectations.
The Components of a Lamination Machine
A lamination machine is designed to protect documents and materials by applying a thin film over them. Understanding its components is essential for effective use.
Key parts of a lamination machine include the feed tray, rollers, and temperature control. The feed tray holds the documents. It guides them into the machine. Rollers are crucial; they apply heat and pressure. This ensures proper adhesion of the laminate. Temperature controls let users adjust settings for different materials.
Tips: Always check if the rollers are clean. Dust can cause uneven lamination. If you notice bubbles, re-evaluate the temperature settings. Sometimes, the film might not adhere properly if settings are incorrect.
Another component is the cooling system, which sets the laminate after the process. This system prevents warping. It's important to monitor its condition. If the lamination isn't cooling correctly, it might affect the quality. Pay attention to these details for best results.
What is a Lamination Machine and How Does It Work? - The Components of a Lamination Machine
| Component | Description | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Laminator Rollers | The heated rollers that apply pressure and heat to the laminate film and substrate. | Heat and compress the laminate film onto the substrate. |
| Feed Tray | The area where the items to be laminated are placed before feeding into the machine. | Holds and aligns the documents for lamination. |
| Control Panel | The interface for setting temperature and speed for the lamination process. | Allows user to adjust settings for optimal lamination. |
| Thermal Fuse | Safety component that prevents overheating. | Protects the machine and user from fire hazards. |
| Output Tray | Where the laminated items exit the machine after processing. | Catches finished laminated items for retrieval. |
How Lamination Machines Operate: A Step-by-Step Guide
Lamination machines are vital in many industries, offering a protective layer to documents and materials. Their operation can seem complex, but it follows several straightforward steps. Initially, the material, often paper or film, is fed into the machine. Industry reports indicate that around 70% of modern businesses rely on lamination for branding and document durability.
Once loaded, the machine heats and melts adhesive layers. The rollers then press the material against the laminating film. This process ensures even coating, critical for effective lamination. However, achieving perfect adhesion can be tricky. Mistakes often occur, resulting in bubbles or peeling edges. These imperfections remind users to regularly calibrate their machines.
After lamination, the output is cut to size. This step requires precision, as uneven cuts can render work unusable. Studies show that up to 15% of lamination projects face such issues. Regular maintenance of the cutting blades can help reduce waste. Attention to detail here is crucial. Striving for perfection often leads to better results, but it requires mindfulness and experience.
Lamination Machine Usage Overview
This bar chart illustrates the usage percentage of lamination machines across various user categories. Small businesses lead in usage due to their frequent need for document preservation, followed by educational institutions and home users.
Types of Lamination Machines and Their Uses
Lamination machines come in various types, each designed for specific needs. A common type is the pouch lamination machine. It uses plastic pouches to encase documents. Users often appreciate its ease of operation. However, the results can vary based on heat settings and pouch quality. Sometimes, documents might not adhere properly, leading to bubbles or wrinkles.
Another type is the roll lamination machine. This is typically used in higher-volume settings. It processes large rolls of film to laminate materials continuously. This machine is great for banners and other large prints. However, it requires careful adjustments. Improper tension can lead to uneven lamination, which can be frustrating.
Cold lamination machines are also available. They do not use heat, making them safer for heat-sensitive documents. They are ideal for photos and delicate materials. Yet, the adhesive may not create as strong a bond as heated methods. Users often report mixed results. Finding the right machine depends on your specific needs and experience.
Benefits and Applications of Lamination Machines
Lamination machines are essential in various industries. These devices protect documents, photographs, and other materials by sealing them in plastic. The lamination process increases durability and enhances the visual appeal of items. According to a recent industry report, the global lamination market is projected to reach $12 billion by 2026. This reflects a growing need across sectors for high-quality lamination.
One of the key benefits of using lamination machines is the preservation of important documents. For businesses, this means keeping contracts and marketing materials in pristine condition. Additionally, lamination provides a waterproof barrier, which is vital for outdoor materials like banners. Lamination enhances colors and helps avoid fading over time. This is crucial for visually-driven businesses, like photography and printing services.
Tips: Always choose the right thickness for your lamination sheets. Thicker sheets offer better protection but can increase costs. Consider your budget and needs carefully.
While lamination has many benefits, there are also challenges. Improper techniques can lead to bubbles or wrinkles. It’s easy to overlook finer details during the process. Regular maintenance of the machine is essential to prevent these issues. Not monitoring the temperature can result in poor adhesion. Always keep a checklist handy for best results.











